Project 5: LabBot: Your Personal Research Assistant
A project designed to facilitate researchers in efficiently skimming through crucial research documents. This is a Large Language Model application that uses existing GPT model and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with the help of LangChain to allow the LLM to give personalized responses to the researcher, using contextualized knowledge.
Github Repository: research-paper-chatbot
Workflow:
- Users can upload new research papers or use previously uploaded papers.
- Uploaded documents are processed by splitting them into smaller chunks and generating embeddings for storage.
- Users can interact with the chatbot by asking questions related to the uploaded documents.
- The chatbot retrieves relevant information from the knowledge base and provides answers with source citations.
Technologies:
- Python Libraries: Utilizes various Python libraries such as Streamlit, LangChain, and OpenAI.
- API Integration: Integrates with OpenAI’s API for natural language processing tasks.
- Local Storage: Stores vector embeddings locally using Chroma for efficient retrieval.
Theoretical Concepts:
-
What is an LLM?
An LLM is a large language model. It is trained on massive datasets and can understand and generate text-based content. LLMs use special types of neural networks called transformers and have billions of trainable parameters. Examples of LLM include:- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) (GPT-3 in June 2020, GTF-4 in March 2023) by OpenAI for text completion and image generation.
- LaMDA - a conversational LLM by Google (May 2021).
- LLaMA - an autoregressive LLM by Meta (Feb 2023, edition 2 IN JULY 2023) for chatting and help with coding.
-
What is Hugging Face?
Hugging Face is an open source collaboration platform for developers who build, train and deploy AI models for everyone to use. Anyone can contribute and improve upon existing models.
Creator: “Clément Delangue (CEO) and Julien Chaumond (CTO) from France founded Hugging Face in 2016 as an “AI best friend forever (BFF)” chatbot via a mobile app for teenagers.” -
What is LangChain?
A generic interface for developing LLM applications. Example: Can help us integrate OpenAI to outside sources like Google Drive, Notion etc. for more personalized use of OpenAI.
Creator: “Harrison Chase, a Harvard graduate in statistics and computer science, co-founded LangChain.” -
What is a Vector Store?
A vector is an array of numbers. When they are used to represent text, these vectors are called embeddings. They map the semantic meaning of words together. They can be stored in vector databases called vector stores. There, these embeddings are stored by being clustered together based on similiarity so can be queried with ultra low latency. -
What is RAG?
RAG is Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It allows LLM to use external data and improve contextual understanding. The LLM queries the vector store to get user’s custom info to give a more personalized response. Example: A company can store it’s policy documents in a vector store. An LLM like GPT from OpenAI can be used to access that vector store when prompted and can give responses specific to that company’s documents.
Key Components of the Code:
- Document Loaders: Supports loading data from different sources such as directories and PDF files.
- Text Splitting: Splits long documents into smaller chunks for processing. [1]
- Embeddings: Utilizes SentenceTransformer [2] for generating vector representations of text.
- Vector Stores: Implements Chroma [3] for storing and retrieving vector embeddings locally.
- GPT AI models: Uses GPT-3.5 Turbo [4] for interacting with OpenAI’s API.
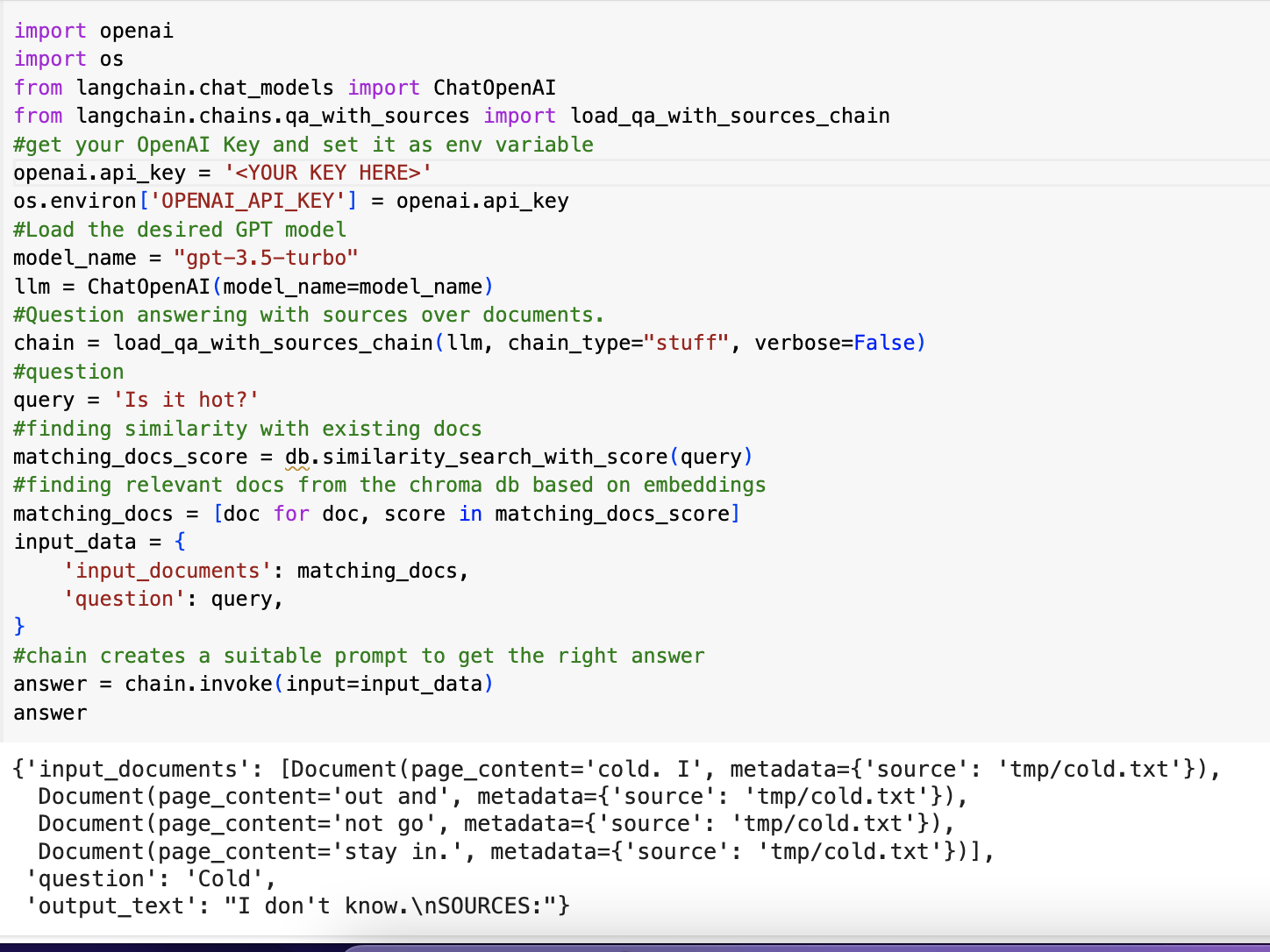
- Question Answering: Provides functionality for question answering over documents with source citations.
- Streamlit UI: The UI is built using Streamlit, allowing users to upload documents, view current knowledge base, and interact with the chatbot.
Appendix:
[1] Text Splitter:
- Using RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
- “The RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter takes a large text and splits it based on a specified chunk size. It does this by using a set of characters. The default characters provided to it are [“\n\n”, “\n”, “ “, “”]. It takes in the large text then tries to split it by the first character \n\n. If the first split by \n\n is still large then it moves to the next character which is \n and tries to split by it. If it is still larger than our specified chunk size it moves to the next character in the set until we get a split that is less than our specified chunk size.”

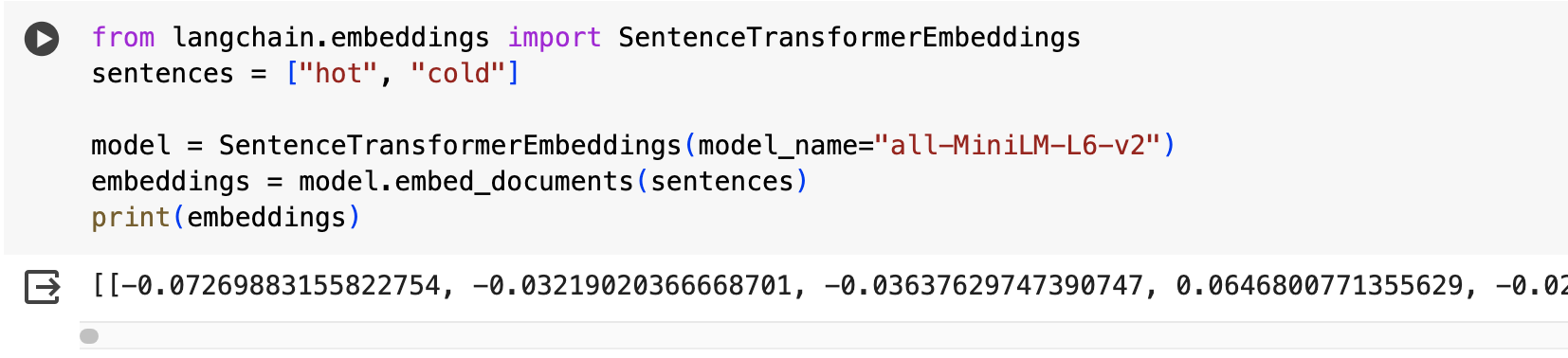
[2] SentenceTransformer:
- Using all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model
- “It maps sentences & paragraphs to a 384 dimensional dense vector space and can be used for tasks like clustering or semantic search.”
[3] Chroma:
- Chroma is a AI-native open-source vector database.
- It can store the vector embeddings on disk (presist directory) created from SentenceTransformerEmbeddings earlier.

[4] GPT AI:
- Using gpt-3.5-turbo model
- “The best model in the GPT-3.5 series. Currently used by the free version of ChatGPT. Cost effective and flexible.” Allows 4,096 max tokens at $0.0015 / 1K input tokens and $0.002 / 1K output tokens.
Appreciation:
I thoroughly enjoyed taking the course LLM Project to Build and Fine Tune a Large Language Model on ProjectPro.
References:
[1] RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
[3] Chroma
[4] GPT AI